Q&A: Cardiologist, Dr. John Colleran on Aortic Aneurysms
An aortic aneurysm can be life-threatening and are more common in older men and smokers than other groups. Dr. John Colleran, with CHI St. Vincent Heart Clinic Arkansas jdiscusses aortic aneurysms.
Dr. Colleran exactly what is an aneurysm?
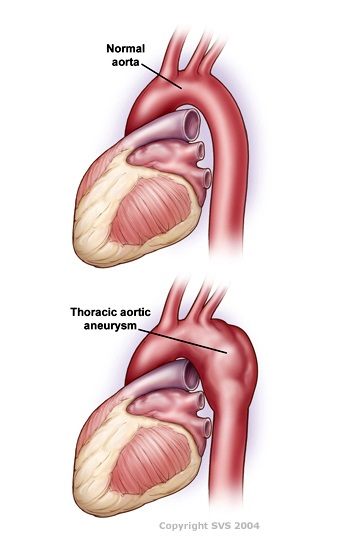
An aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the wall of an artery, in an area where the muscle of the artery is weak. A healthy artery is thick and muscular and can function under the pressure of the heart pumping blood through it. Sometimes aneurysms develop in blood vessels, but they are more common in the aorta, which is the largest artery in the body. There are two places along the aorta where aneurysm can occur. A thoracic aneurysm occurs in the area of the chest. But the more common aortic aneurysm occurs in the part of the aorta located in the middle to low abdomen.
How serious is an aortic aneurysm?
If they are small there is usually no risk, but the risks increase if there are other medical problems. If there is hardening of the artery from the formation of plaque the aorta can become weaker. A blood clot could form at that location, dislodge and increase the risk of stroke. If the aneurysm gets larger it could press on other organs causing pain. And finally the most serious risk is that the aneurysm breaks or ruptures. A ruptured aortic aneurysm is life-threatening.
What causes aortic aneurysms?
We mentioned one of the causes earlier – hardening of the arteries. Other causes are hypertension, an injury, growing older or being born with an abnormality. People with Marfan syndrome and people born with two aortic valvular leaflets fused together, called bicuspid aortic valve, are also at risk for aortic aneurysm. An injury can also cause aneurysm.
What are the symptoms of an aortic aneurysm?
Sometimes there are no symptoms at all. But people with symptoms may feel a tearing pain in the chest, abdomen or between the shoulder blades in the back. A thoracic aneurysm might cause shortness of breath, a cough, trouble swallowing and you might be hoarse.
If an aneurysm ruptures you could become unconscious, have a stroke or heart attack or go into shock. If you have any of these symptoms that occur suddenly, you should get medical attention immediately.
How are aortic aneurysms diagnosed?
Some aortic aneurysms are found during a routine examination by your doctor. A thoracic aneurysm might cause a heart murmur, which your doctor might find. If you have an aortic aneurysm, you might feel as though you have a heartbeat in your stomach. A heart murmur or a sensation of a heart beat in your stomach would signal your doctor to look for an aneurysm. If one is found your doctor will monitor it carefully and recommend repair when it is more than five centimeters wide. Your doctor might use ultrasound, angiography, an MRI or a CT scan to monitor your aneurysm.
What is the treatment for a larger aneurysm?
If it becomes large, or you have symptoms, the weak part of the aorta can be removed and replaced with artificial material. If the aneurysm is close to the aortic valve, your doctor might recommend valve replacement as well.
Is repairing an aneurysm a difficult procedure?
Yes, and it requires an experienced surgeon. The repair is done through open-chest and abdominal surgery. Most people are in the hospital for about five days. For the best outcome you should adopt a heart healthy lifestyle that includes healthy eating and regular exercise.
If you know you’re at risk, what precautions should you take?
If you have hardening of the arteries you should be checked regularly by your doctor. Also aortic aneurysms tend to run in families. So if your parents or siblings have aortic aneurysm you should tell your doctor so the two of you can work together to ensure your best health. You should quit smoke, or never start and adopt a healthy lifestyle.
Dr. John Colleran is a cardiologist at CHI St. Vincent Heart Clinic Arkansas. To make an appointment with him, call 501.255.6000.
